Breaking the Ketosis Code: Why Am I Not In Ketosis and How to Get Back On Track
Breaking the Ketosis Code: Why Am I Not In Ketosis and How to Get Back On Track
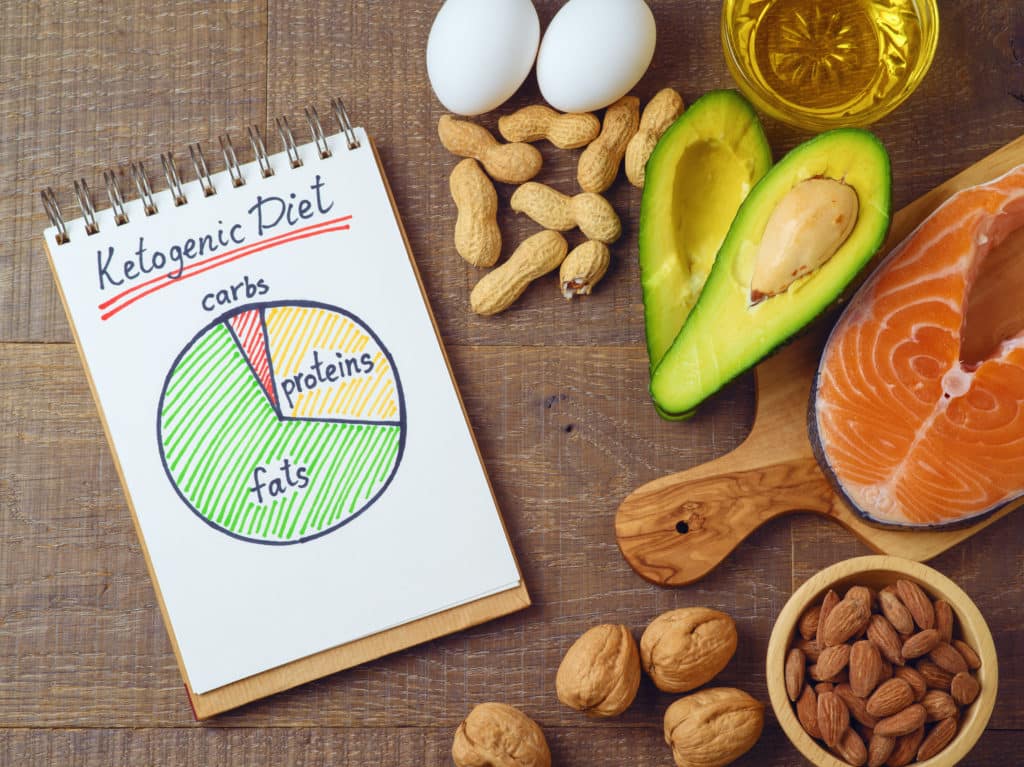
The ketogenic diet is a popular low-carb, high-fat diet that has been shown to promote weight loss, improve metabolic health, and enhance cognitive function. However, despite its many benefits, some people may struggle to enter ketosis, the metabolic state in which the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. If you're one of these individuals, don't worry - there are several reasons why you may not be in ketosis and plenty of tips for getting back on track.
How You Enter Ketosis
Before we dive into the reasons why you may not be in ketosis, it's important to understand how the body enters this metabolic state. Ketosis occurs when the body is deprived of glucose, its primary source of energy, and begins to produce ketones from stored fat instead. This process is typically triggered by following a strict low-carb, high-fat diet that forces the body to use fat for fuel.
Measuring Ketones
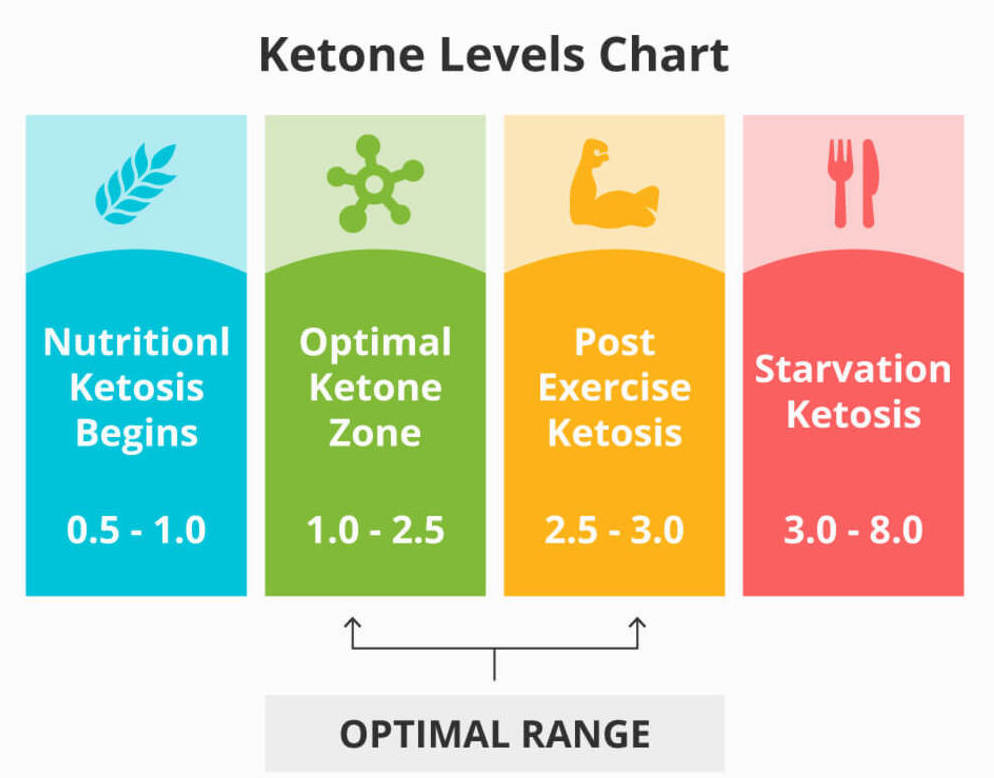
One way to determine whether you're in ketosis is to measure your blood ketone levels using a ketone meter. Ideally, blood ketone levels should be between 0.5 and 3.0 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) to indicate that you're in a state of nutritional ketosis. However, it's important to note that blood ketone levels can fluctuate depending on factors like exercise, meal timing, and overall carb intake.
Why Am I Not In Ketosis?
Now, let's explore some of the reasons why you may not be in ketosis despite following a low-carb, high-fat diet:
Tips For Getting In Ketosis
If you're not in ketosis and want to get back on track, here are some tips to help you reach your goals:
In conclusion, entering and maintaining ketosis requires a strict low-carb, high-fat diet and careful attention to your macronutrient intake. If you're struggling to enter ketosis, it's important to reassess your diet and make adjustments to ensure that you're consuming the right balance of carbs, protein, and fat.
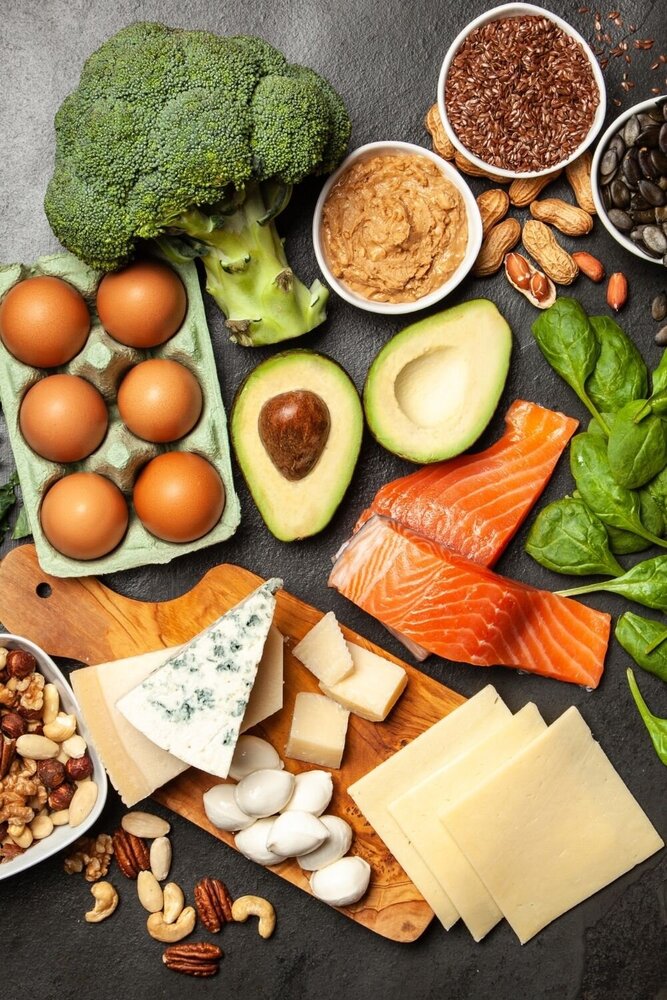
Ketosis Foods
When it comes to entering and maintaining ketosis, the types of foods you consume play a crucial role. The ketogenic diet emphasizes low-carb, high-fat foods to promote the production of ketones in the body.
Some examples of ketosis foods include:
By focusing on these types of foods and avoiding high-carb foods such as bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, you can promote the production of ketones in your body and enter and maintain ketosis more easily.
Following a well-planned ketosis meal plan can be an effective way to ensure that you're consuming the right balance of foods to promote ketosis and achieve your health goals. When creating a ketogenic meal plan, it's important to focus on low-carb, high-fat foods and to limit your intake of carbs to 20-50 grams per day.
Here's an example of a one-day ketosis meal plan:
While this is just one example of a ketogenic meal plan, there are endless possibilities when it comes to creating a keto-friendly diet that fits your tastes and preferences. By focusing on healthy, high-fat foods and limiting your intake of carbs, you can promote the production of ketones in your body and achieve your health and wellness goals.
Remember, it's important to track your macronutrient intake using a tool such as the Salmo app to ensure that you're consuming the right balance of carbs, protein, and fat to stay in ketosis. Additionally, don't be afraid to experiment with different recipes and meal ideas to keep your diet interesting and enjoyable.
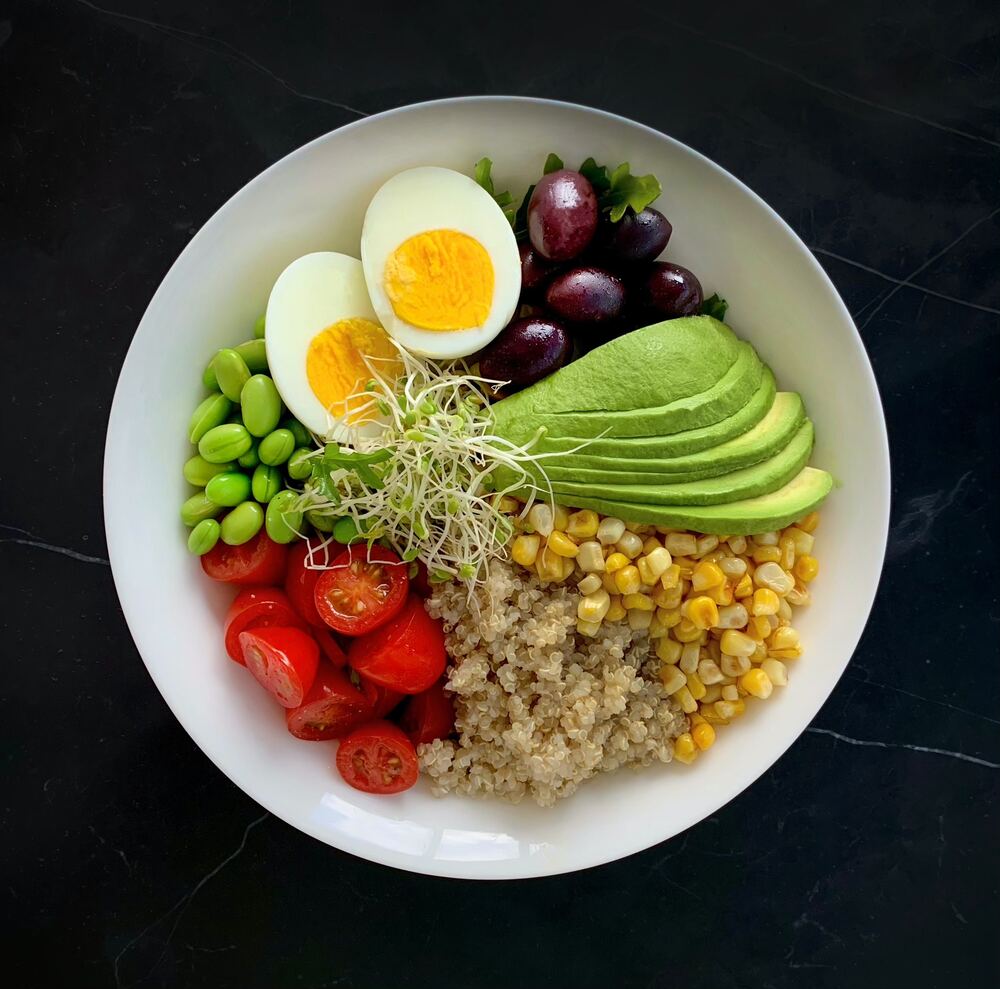
Examples of Ketosis Meals
These are just a few examples of the many delicious and satisfying ketosis meals that can be enjoyed on a ketogenic diet. By focusing on healthy fats, moderate protein, and low-carb vegetables, you can create a varied and satisfying meal plan that promotes ketosis and supports your health and wellness goals.
In addition to tracking your macronutrient intake and focusing on healthy, high-fat foods, there are other steps you can take to help your body enter ketosis. For example, incorporating intermittent fasting into your routine may help to increase ketone production and enhance fat burning. Additionally, engaging in regular exercise can help to deplete glycogen stores and promote the use of stored fat for fuel.
If you're still struggling to enter ketosis despite making dietary and lifestyle changes, it may be helpful to speak with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Overall, while the ketogenic diet can be an effective tool for weight loss and overall health, it's important to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed to ensure that you're able to enter and maintain ketosis safely and effectively. By following a balanced, low-carb, high-fat diet and incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, you can harness the power of ketosis to reach your health and wellness goals.
Might be interesting - The Ultimate Guide to Tracking Macros on Keto for Effective Weight Loss